
There is general agreement that smaller units of government are more responsive and accountable to their electorates. However, proponents of larger governments often claim that this advantage also creates higher spending and tax levels. On this basis, bigger-is-better proponents often suggest consolidating local governments to save money. Such calls have increased in recent years, with the unprecedented fiscal difficulties faced by governments from the federal to local level. However, more often than not, nothing more underlies consolidation proposals more than an interest in reducing the number (count) of local governments. It is largely taken as an article of faith that larger governments save money relative to smaller governments.
Ohio has had more than its share of local government consolidation proposals. The Ohio Township Association asked us to review local government financial performance in the state. We were able to confirm that Ohio's smaller governments are, on the whole, more responsive and accountable. However, the analysis clearly showed that smaller local governments have materially better financial performance.
We analyzed per capita financial measures for all reporting local general purpose governments in the state, using Auditor of State data (Note). Ohio has three types of general purpose governments. Cities are incorporated municipalities with 5,000 or more population in the last federal census. Villages are incorporated municipalities with less than 5,000 population. The balance of the state is made of townships, which have virtually the same powers as municipalities.
The Efficiency of Smaller Local Government
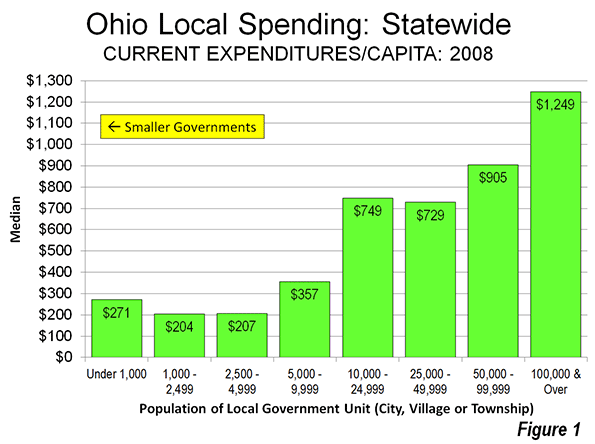
The data indicates that smaller units of local government have median spending per capita that is less than larger local governments. Local governments with more than 10,000 population spent an average of at least twice that of smaller governments. The lowest per capita spending was in local governments with between 1,000 and 4,999 population (Figure 1).
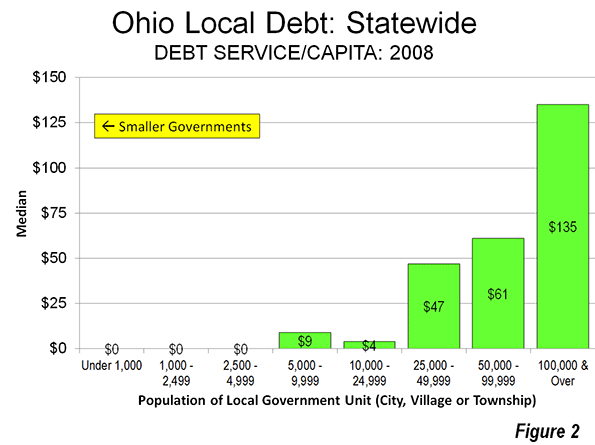
The smaller government advantage extended to debt. The median debt service per capita for local governments with fewer than 5,000 population was zero, while the median debt service per capita for local governments with 10,000 to 25,000 population was under $10 annually (Figure 2).
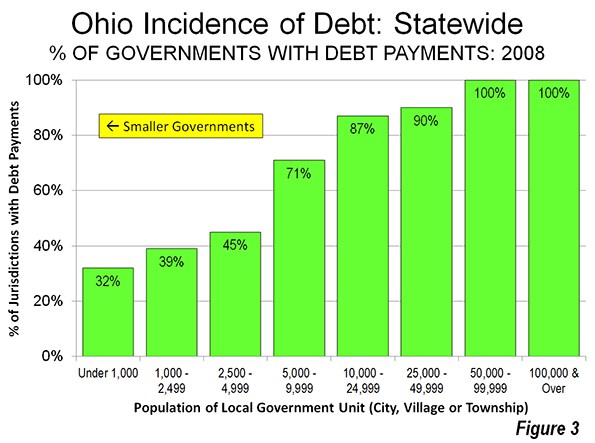
The incidence of debt was also less among smaller local governments. Fewer than one-half of the local governments under 5,000 population had any debt. In contrast, all of the local governments with 50,000 or more population had debt (Figure 3).
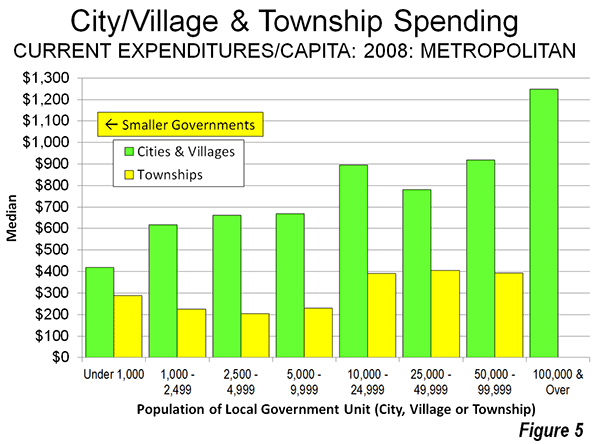
Smaller Governments Excel in Metropolitan Areas
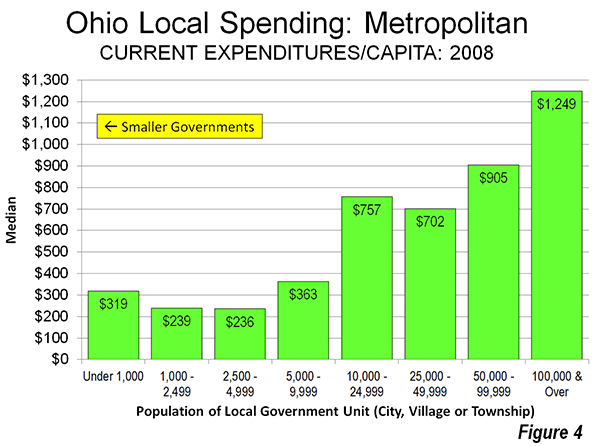
It might be thought that this smaller-is-better relationship stems from the more rural setting of some smaller local governments. However, an analysis of local government spending and debt per capita within metropolitan areas indicates the same conclusion: smaller governments spend less and borrow less per capita (Figure 4).
Townships: Even Less Costly
Townships have been a particular target of "bigger-is-better" consolidation proposals, perhaps because of their smaller average population. Yet, despite their much larger average service areas (in square miles), townships represent a far smaller share of local government spending than their population share. Townships account for 11 percent of local general purpose government spending (excluding counties), yet have 35 percent of the state's population.
Townships have lower current expenditures per capita than villages and cities in all but one population category. In metropolitan areas, townships spend less per capita in all population categories (Figure 5). In addition, townships have lower per capita debt service payments than cities and villages
The lower per capita spending of townships is attributable, at least in part, to lower administrative costs and lower labor costs per capita. Further, as with smaller municipalities, taxpayers often do not often demand the same level of service that is provided in the larger cities.
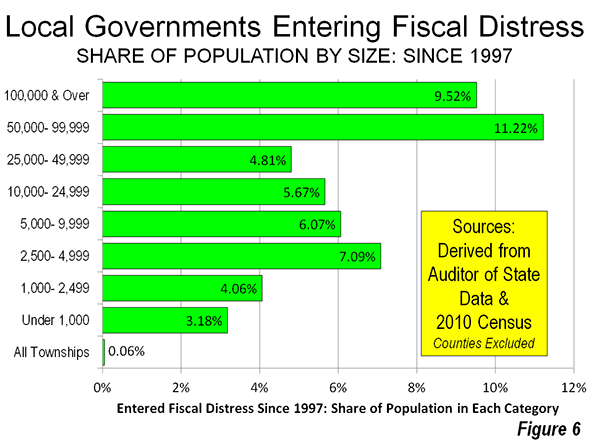
Small Government: Less Likely to Enter Fiscal Distress
Smaller local governments have experienced financial distress less. After the city of Cleveland bankruptcy in the 1970s, the state established the Local Government Fiscal Distress, which identifies local governments in serious distress and aids them in returning to normal fiscal health. The smallest cities and villages entered the Fiscal Distress program at a rate less than one-half that of the largest governments. The townships did even better. Only two of the state's more than 1,300 townships were placed in the Local Government Distress Program (Figure 6).
Why Larger Local Governments are Less Efficient
One of the reasons that larger governments spend and borrow more is that they are less accessible to taxpayers and more accessible to interests which benefit from higher spending. This can lead to a vicious cycle that drives taxes so high that governments borrow more, followed by proposals to consolidate when the borrowing capacity becomes more constrained. Further, the very size of some larger governments can make them "too big to fail," like large financial institutions in the Great Financial Crisis. This can lead to "bailouts" by state taxpayers. Ohio's Local Government Distress Program is an attempt to avoid these difficulties, by providing technical assistance and guidance.
Smaller governments that consolidate face two critical challenges likely to increase costs. The first is that labor costs tend to be "leveled up" to the compensation levels in the higher cost jurisdiction. The other problem is that services and service levels also tend to be "leveled up."
Proponents of consolidation sometimes assume that a large number of governments results in duplication of services. However, each of the local governments have exclusive service areas. For example, garbage is not collected by multiple jurisdictions to the same addresses. Smaller jurisdictions also tend to employ more part time staff, and even volunteers, especially in fire departments. Another advantage of smaller governments is that their elected officials are able to more directly manage the business of a smaller jurisdiction, because they do not have to rely more on intermediate staff.
The performance of Ohio's smaller governments shows that there is no need to choose between accessible government and efficient government. Ohio's smaller local governments deliver both.
Wendell Cox is a Visiting Professor, Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, Paris and the author of “War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life.”
-----
Note: These do not include counties, school districts or special districts.
Illustration: Great Seal of the State of Ohio (from http://www.netstate.com/states/symb/seals/images/seal_ohio2.jpg)













She say!
She say!