
While not immune to the recession, the upper Great Plains is in a different economic situation from the rest of the nation. Growth coupled with low unemployment means more strain on the region’s workforce, making it tougher for employers to find the workers they need. It's not so much about jobs anymore, but about finding the right workers.
Since 2008, the region covered by Prairie Business Magazine – North Dakota, South Dakota and western Minnesota – has grown its employment by 1.8 percent, compared to a loss of 2.5 percent across the country. In addition to that growth, North Dakota alone has 21,000 unfilled jobs.
To determine some of the toughest jobs to fill in the region in the past year we used data compiled by EMSI, Inc., a model that includes a combination of over 90 state and federal sources and includes estimates of independent contractors and others. We looked at a number of metrics, including the number of openings in the region due to growth, retirements, and turnover; the number of openings compared to the total jobs in an occupation; and the regional concentration of a job here compared to the rest of the nation.
The occupations are separated into five groups: construction, extraction, transportation and material moving; business, finance and office; heath care; science, mathematics, engineering and computer; and manufacturing occupations.
The construction, resource extraction and transportation category is not surprisingly dominated by the ongoing energy boom in western North Dakota. Roustabouts lead the way with 917 new jobs and 979 total openings in the past year. Other oil-related jobs such as service unit operators (781 openings), derrick operators (511), rotary drill operators (479), extraction helpers (335) and wellhead pumpers (295) all have openings above 40 percent of its 2010 employment level. We read a lot about the stress on the labor force in that region, but the numbers are astounding.
The overall leader in total job openings across the region is heavy truck drivers, with 1,973 openings from 2010-2011. The need is most acute in oil country, but the entire region has a 70 percent higher concentration of heavy truck drivers than the national average. Of the 152 counties in our analysis, 138 have a higher concentration of heavy truck drivers than the national average.
The national media has credited the oil boom for the economic growth. The economic benefits of the energy boom have spread across the region, but there is more to the story. While the entire region trailed the nation in job growth until 2007, the region’s five largest metropolitan areas – Bismarck, Grand Forks, Fargo, Sioux Falls and Rapid City – were well ahead of the nation through the entire decade. Now containing 39 percent of the regional jobs, these five metropolitan areas beat the nation in job growth over the decade by 10 points, 15.8 to 5.8 percent.
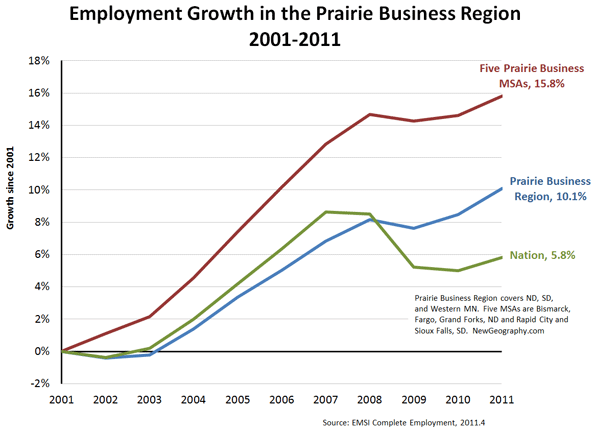
It’s not just growth in retail and food service jobs. Over the past decade the five metropolitan areas added 8,000 jobs in professional, technical, and scientific services, nearly 18,000 in health care, and 8,000 in finance, with each sector paying roughly $50,000 per year. The region also added 1,500 jobs at management offices and corporate headquarters making an average of $80,000 per year. It’s time that parents in our region stop telling their kids, “you need to leave the state to find a good job.” We need to improve efforts to help students and displaced workers understand the emerging options available in the region.
The Prairie Business region has also become a growth center for science, math, engineering and computer occupations, adding nearly 18 percent to its technical workforce in the past decade, compared to just 3.6 percent growth in the rest of the nation. The growth rate in the five metropolitan areas was more than 27 percent. Some of the most in-demand jobs include industrial engineers (91 openings), mechanical engineers (87), geological engineers (52), petroleum engineers (50) and geoscientists (45). A new program for petroleum engineers at the University of North Dakota School of Engineering and Mines may help address the shortages in these fields.
This strong growth in engineering and technical jobs is tempered somewhat because the region still lags the nation in these occupations. The biggest gaps are in bachelor’s degree level information technology and software fields, where the region trails the nation by 25 to 40 percent in many occupations. While the region’s high growth rates are encouraging, there is still plenty of ground to make up. At the same time the region is highly concentrated in many two year level technical jobs, creating a solid foundation for technical industries to build on.
The region’s manufacturing economy was hit hardest by the recent recession, but was booming in the six years prior and is now recovering. In demand production occupations include welders (677 openings), assemblers (604), supervisors (194), machinists (156), computer-controlled machine tool operators (107), and engine assemblers (88).
Across the region, 52 of the 152 counties hold an above average number of production jobs. Hot spots in the region include Jerauld, Yankton and Brookings counties in South Dakota; Roseau, Nobles and Kandiyohi in Minnesota; and Sargent and Richland in North Dakota.
Workforce and economic development agencies, educators and trainers, and the business community need to continue to actively collaborate to share information and create partnerships across state lines. Private businesses must be open to working with training and placement agencies to communicate their needs, and regional governments must be open to creating more flexible funding sources for specialized training. Educational institutions are beginning to use the ample labor market data available to tailor programs to fit the need of the region’s economy.
Ultimately, the talent narrative in the region needs to shift away from “retaining our young people” towards recruitment of young families. Demographic data confirms the greatest shortage across the region is those age 35 - 44, and employers are reporting troubles recruiting mid-career professionals. Migration data shows that the net loss from North and South Dakota to the Minneapolis region has stopped in the past two years. The Prairie Business region is showing signs of turning the economic and demographic corner. It is now time to act to sustain the region’s long-term future.
This piece originally appeared in Prairie Business Magazine.
Mark Schill is Vice President of Research at Praxis Strategy Group, an economic development and research firm working with communities and states to improve their economies. He is Managing Editor of NewGeography.
Fargo photo by David Kohlmeyer.












