What if the region we broadly understand as the Midwest, stretching from the foothills of the Alleghenies to the high plains, and from the chilly northern Great Lakes to the Ohio, Mississippi and Missouri river valleys, had been allowed to develop as organically as its eastern and southern -- and even western -- neighbors?
If it had, it would be far better understood, have a much stronger cultural clarity, and more recognized for its contributions to American society and economy.
Here's what I mean. The north central region of the U.S. has been an American paradox since its founding. Unlike other regions of the country, where a critical mass of settlers established a colony or territory and then pursued legitimacy, the core of the region had its territorial boundaries established long before settlers had a chance to make a major imprint on the land. That set off a race for control of the region by two already established regions, New England and Appalachia, with vastly different motivations -- and cultural mores. Because they came from different places, they took different paths to the Midwest. New Englanders came via the Erie Canal and Great Lakes, while Appalachians traveled northward across the Ohio River. Rather than intermingle and create a new and blended society, the New Englanders and Appalachians tended to maintain their local strongholds, with New Englanders in larger Great Lakes cities, and Appalachians in the upper regions of the Ohio Valley. And this happened without any reconsideration or adjustment of political boundaries in the Midwest's early days.
This has hampered our understanding of the Midwest ever since.
Here's a thought experiment. Let's say that instead of New York expanding to the shores of Lake Ontario and Lake Erie because it wanted to control development of the Erie Canal, western New Yorkers fought to establish their own state. Similarly, let's say that early settlers of western Pennsylvania recognized their remoteness from Harrisburg and Philadelphia, and decided local control suited them, too. And let's further suggest that, instead of becoming part of Ohio, the Connecticut Western Reserve was also allowed to develop as a separate state as well.
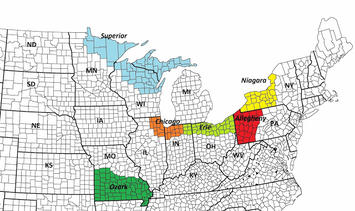
Ultimately, it's conceivable that a new map of the Midwest, one that matches more closely to actual American settlement patterns, might look something like this:
In my mind, as many as six new states could have emerged. Western New York could've become Niagara, with Buffalo and Rochester as its key metropolises. Western Pennsylvania could've become Allegheny, centered on Pittsburgh and Erie. The Connecticut Western Reserve could've become Erie (or Cuyahoga?), greater Chicago could've been recognized as its own state, and the upper parts of Michigan, Wisconsin and Minnesota could've become Superior. The southern part of Missouri could've become Ozark.
The benefit of this is that the political environment aligns with the settlement patterns and modern-day networks of the region. I've made similar points before about the cultural geography of the Midwest. I think that because two different cultural groups inhabited the same space without ever effectively coming together, they've never maximized the development potential within either. Yes, the Midwest was the nation's manufacturing center for much of the 20th century, but it could be argued that it often did so in spite of rural and agricultural interests that were strong in state capitals like Columbus, Indianapolis and Springfield. When manufacturing faded, those same interests often promoted the development of cities within their regions that were less tainted by a manufacturing legacy.














