For years, economic and social observers have taken to redrawing our borders to better define our situation and to attempt to predict the future. Maybe you thought the global financial meltdown has raised anxiety levels in the United States quite enough. But a Russian professor’s decade old prediction of national disintegration suggests much worse on the way.
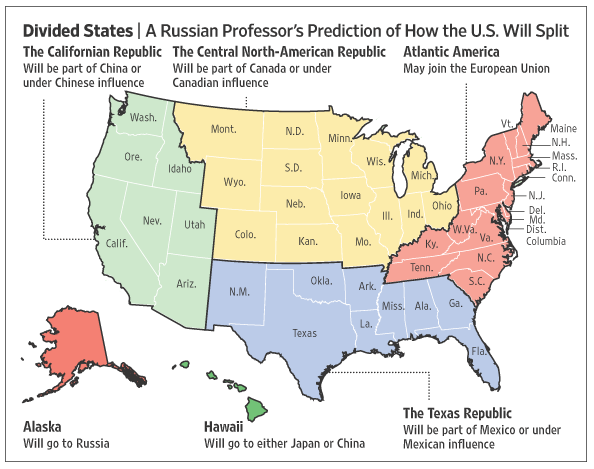
Prof. Igor Panarin, a 50-year-old former KGB analyst and a dean of the Russian Foreign Ministry’s academy for future diplomats, estimates there’s a 45-55% chance that the United States will disintegrate like the Soviet Union did sometime in 2010. Mass immigration, economic decline and moral degradation will trigger civil war, the collapse of the dollar and massive social unrest. This in turn will lead to the U.S. breaking into six blocs — with Alaska reverting to Russian control – and other foreign powers grabbing other pieces.
Panarin’s new map of the United States puts the "Californian Republic" under China's influence, "the Texas region" under Mexico's. Hawaii will come under Japanese or Chinese rule, East Coast states will join the European Union, while central northern parts of the US will gradually come under Canada's influence.
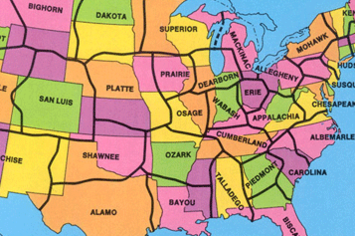
A less sinister revision of the states that comprise the republic occurred in the 1970s when geography professor C. Etzel Pearcy proposed redrawing the borders of the US states, reducing them from 50 to 38. Pearcy’s framework casts aside the convenience of determining boundaries by using the land's physical features, such as rivers and mountain ranges, or by the simple usage of latitude and longitude. Instead, his realignment gives high priority to contemporary population density, location of cities, lines of transportation, land relief, and size and shape of individual States.
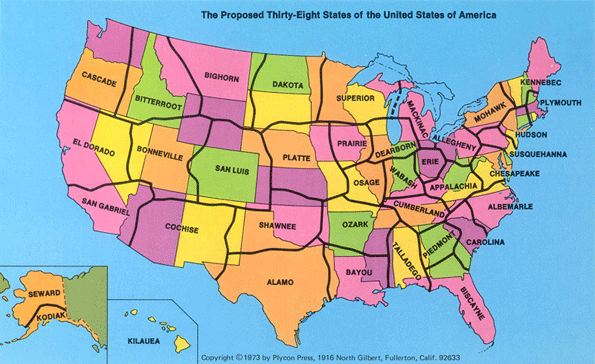
In the current fiscal climate some see the new 38 state map as inspired. According to Pearcy, 25% of the expenditures by states can be attributed to the fixed costs associated with the support and maintenance of state governments themselves. For at least some states this kind of savings could be very appealing right now.
Rethinking, reimagining and then redrawing the borders of maps is by no means a new or even fruitless endeavor. That some if not many borders are where they are for seemingly meaningless or irrational reasons is obvious. Mark Stein’s How the States Got Their Shapes, for example, documents how natural features like rivers come together with the dreams and schemes of people to create today’s jigsaw puzzle of states. Gerrymandering borders for political, economic or religious reasons is both a historical and contemporary reality.
Any economic planner or strategist worth their salt understands, of course, that borders on a map seldom represent or hold sway over how the real economy operates. Sure there are tangible differences in taxes, regulation and all the things that make up a business environment. But like water, economic activity goes where it wants and finds its own level. This has lead to an increasing amount of policy attention being given to cross-border territories of regions, zones, corridors, clusters, networks and the like.
North America Re-Imagined
One of the more reasoned, enduring efforts to make sense of a borderless economic and cultural landscape is Joel Garreau’s landmark work on the The Nine Nations of North America. My 27 year-old copy’s dust jacket asks the reader to forget the traditional map and consider the way North America really works because new realities of power and people are remaking the continent.
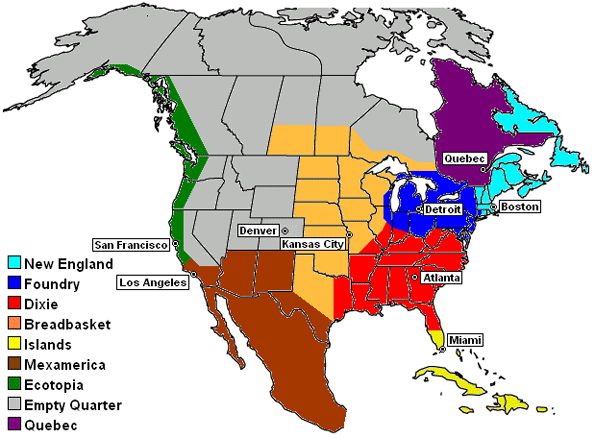
A recent conference on USA/Canada cross-border economies in the Great Plains confirmed that Garreau’s analysis continues to influence thinking on regionalism. The longevity of his regions lies not only on their basis in actual data but also tied to the distinct “prisms” though which each nation sees the world.
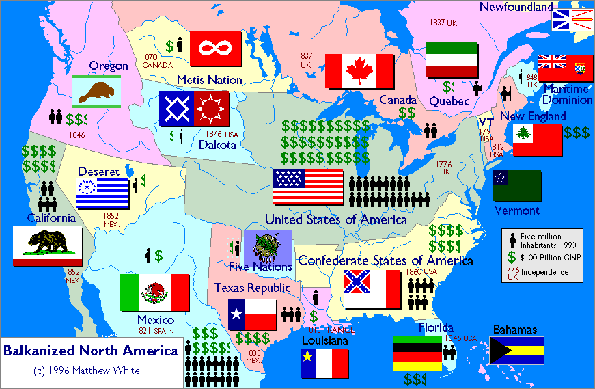
What could have been in North America, instead of how things really are, is the subject of Matthew White’s 1997 map of a balkanized continent. Here the basic premise is that, in an alternate history beginning in 1787, the westward expansion of the Anglo-American people proceeded pretty much as it did, but the United States government just couldn't hold the country together against separatists.
How North America really works and how that is manifested spatially has generated growing interest of late and is reflected in the emergence of cross-border networks and organizations. The government of Canada recently issued an exhaustive report titled The Emergence of Cross-Border Regions Between Canada and the United States: Reaping the Promise and Public Value of Cross-Border Regional Relationships. Here the interest is certainly not on redrawing the borders but on recognizing and building on shared socio-cultural values and furthering relationships between businesses, first and foremost, and universities.
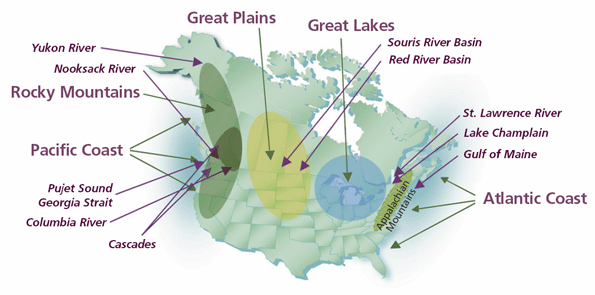
Mostly a bottom-up phenomenon, these cross-border regional relationships are evidenced by the growth of both informal relationships and formal networks and a rise in cross-border regional co-operative mechanisms. From a policy standpoint the existence of cross-border regions requires new ways of thinking about development, going well beyond our parochial perspective. And this sort of thinking is important because regions – like economic fields of activity – represent the primary theatre in which most activities of international trade and economic integration actually take place.
Map Forth
Thematic maps that reconfigure our geography can intrigue and fascinate us. They are really, as some have said, graphic essays that portray spatial variations and interrelationships of geographical distributions. As noted by Norman Joseph William Thrower in Maps and Civilization: Cartography in Culture and Society, thematic maps use the base data of coastlines, boundaries and places, only as point of reference for the phenomenon being explained.
Sometimes maps can inspire and motivate us by helping to more fully understand the geography of our economic and demographic challenges and opportunities. Perhaps most importantly thematic maps tell a story about places. Some describe the way things really are now while others express a vision of the future. In both cases they can be a graphical point of departure for plans and actions that help us to make the places we inhabit better places to live and work.
Delore Zimmerman is president and CEO of and publisher of Newgeography.com













vision without glasses
vision without glasses Vision Without Glasses: How To Achieve Near Perfect 20/20 Vision Completely Naturally, No Matter How Young Or Old You Are. This site is a leading resource for information about the Duke Peterson Vision Without Glasses PDF book that teaches you simple and highly effective eye exercises to improve vision and other techniques to get better eyesight without glasses or contact lenses.
learn more at rebelmouse The
learn more at rebelmouse The Fantasy Lover Formula System: Become Your Woman's Ultimate Sexual Pleasure. This site is a leading resource for information about the Krista and Leann Fantasy Lover Formula PDF book and video seduction system that teaches you incredible techniques on giving intense sexual pleasure to your wife, girlfriend, or hottie you just met at the bar.
john kiefer carb backloading
john kiefer carb backloading Carb Backloading Diet: What Muscle And Fitness Magazine Has Described As "Eat Like A Pig. Get Shredded. The Carb Backloading Diet Could Provide The Holy Grail Of Packing On Mass Without Adding Fat." This site is a leading resource for information about the John Kiefer Carb Backloading 1.0 PDF book and body fat control system that teaches you how to pack on incredible muscle while burning fat simultaneously, all while enjoying the foods you love...and YES that means pizza and donuts!
Another good map, user-produced
Visit http://www.commoncensus.org. Produced by a friend of mine. Excellent site, the map self-draws based on user input.