Yesterday’s Midterms were not a victory for conservative or progressive ideology, but an assertion of the growing power of geography in American politics. It was less a national election than a clash of civilizations.
Virtually nowhere in blue areas did Republicans make gains. Both the north-east and California – the central players in Democratic Party politics – stayed solidly blue. Even the most well-regarded GOP candidates, such as Lanhee Chen who ran for California state controller, struggled to make inroads in Democratic territory.
Meanwhile, the senators and governors of the leading red states – Texas’s Greg Abbott, Georgia’s Brian Kemp, Florida’s Ron DeSantis, Ohio’s Mike DeWine – all won handily. Almost all blue-state governors remained the same as well, although the Democratic incumbents often won by smaller margins.
So, what is happening in this increasingly inexplicable country? Essentially, there are now two prevailing realities in the US. One is primarily urban, single and, despite some GOP gains in this demographic, still largely non-white. It functions on the backs of finance, tech and the service industries. The other is largely suburban or exurban, family centric and more likely involved in basic industries like manufacturing, logistics, agriculture and energy.
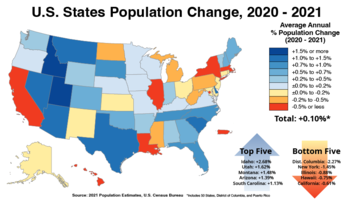
Usually, the media assume these two Americas represent equally viable political economies. But this is increasingly not the case. In population terms at least, red America is now growing far more rapidly than blue America. And this makes it more important politically. Since 1990, Texas has gained eight congressional seats, Florida five and Arizona three. In contrast, New York has lost five, Pennsylvania four and Illinois three. California, which now suffers higher net outbound-migration rates than most Rustbelt states, lost a congressional seat in 2020 for the first time in its history.
This decline in blue America has accelerated since the pandemic, due to rising crime and the availability of remote work. Last year, New York, California and Illinois lost more people to outbound migration than all other states. Demographer Wendell Cox notes that the largest percentage loss of residents has occurred in big core cities such as New York City, Chicago and San Francisco. In contrast, population burgeoned in sprawling areas such as Phoenix, Dallas and Orlando.
The future of the GOP depends on the continued growth of such places, as well as the growth of suburbia nationwide. Between 2010 and 2020, 51 major metropolitan areas lost 2.7million net domestic migrants from their most central counties, while suburban counties gained two million people. The Midterms show that Republicans are gaining ground in these largely suburban areas – particularly in Florida, as well as suburban Phoenix, the outskirts of Atlanta, the Houston exurbs, largely suburban Nashville, the sprawling Virginia Beach area and suburban Detroit. Democrats, where they made gains yesterday, tended to be in places like California, where the Republican Party has all but ceased to exist.
Read the rest of this piece at Spiked.
Joel Kotkin is the author of The Coming of Neo-Feudalism: A Warning to the Global Middle Class. He is the Roger Hobbs Presidential Fellow in Urban Futures at Chapman University and Executive Director for Urban Reform Institute. Learn more at joelkotkin.com and follow him on Twitter @joelkotkin.
Chart: Abdullah Ali Abbasi via Wikimedia under CC 4.0 License.












