NewGeography.com blogs
Jo Becker and Gretchen Morgenson (she reported on the lack of mortgages behind mortgage-backed securities) did a long piece on Treasury Secretary Timothy F. Geithner in the New York Times. They paint a stark picture of Secretary Geithner’s brand of “Collusive Capitalism”: lunch at the Four Seasons restaurant with execs from Citigroup, Goldman Sachs and Morgan Stanley; private dinners at home with the head of JPMorgan Chase.
Most importantly, Becker and Morgenson raise the question of why – with all that frequent contact – Geithner never sounded the alarm about these banks? Indeed, as I’ve pointed out before, Geithner took no steps to prevent $2 trillion in US Treasury bond trades go unsettled for 7 months – until it was over, when he called a meeting of the same bankers that caused the problem to have them do a study, take a survey, make some suggestions, etc. The one action that needed to be taken – to enforce finality of settlement – was never on the table.
When the banks behaved recklessly in lending, trading, issuing derivatives and generally fueling the Bonfire of their Vanities, according to Becker and Morgenson, Geithner’s idea was to have the federal government “guarantee all the debt in the banking system.” As Martin Weiss asks in his ads for Money and Markets, “Has U.S. Treasury Chief Geithner LOST HIS MIND?”
Since 1998, most major American metropolitan areas have seen a decline in employment located close to the city center as jobs have moved farther into the suburbs.
A recent report by the Brookings Institution determined that this “job sprawl” threatens to undermine the long-term regional and national prosperity.
The report analyzes the spatial distribution of jobs in large metropolitan regions and how these trends differ across major industries, in addition to ranking cities according to their amount of job sprawl.
The report found that only 21 percent of employees work within three miles of downtown. Using the period before the current recession, the report found that while the number of jobs has increased, 95 of 98 metro areas analyzed saw a shift of jobs away from the central core.
The Brookings Institute argues that “allowing jobs to shift away from city centers hurts economic productivity, creates unsustainable and energy inefficient development and limits access to underemployed workers.” Yet this may be more a matter of Brookings ideology than a likely far more complex reality.
Job sprawl is greatest both in areas that have clearly declined – such as Detroit – as well as growing regions like Dallas-Fort Worth. Nor does concentration guarantee success, as can be seen by the mediocore performance of the more concentrated New York region. Yet virtually everywhere jobs continue to sprawl, in many cases faster than even population. Maybe it’s time to learn how to adjust to the emerging future rather than yearn for a return to the economic and geographic structure of the last century.
The Illinois state budget is on life support, with a $4 billion shortfall projected for this year and even more in 2010. So what’s a state to do?
In a move that has some scratching their heads, Governor Pat Quinn has proposed an increase on the tax rate for both personal and corporate income tax.
For a state ranked 48th in overall economic performance and 44th in economic outlook, such a tax hike seems questionable. Corporate and personal income is lagging. According to a recent study, non-farm payroll employment has only risen 3.6 percent and the growth of per capita income ranks 39th in the nation.
The state’s private sector is largely responsible for fueling a well-funded public sector. Such a tax increase could further suffocate growth, which in turn will impact the public sector as well.
Along with its persistent corruption, Illinois’ poor economic showing may become yet another embarrassment to an administration whose top leadership comes from the increasingly bedraggled Land of Lincoln.
It also wasn’t that long ago that Congress held hearings on the bonuses paid to AIG employees after the bailout. Now, according to New York Times reporter Louise Story Wall Street compensation is rising back to where it was in 2007 – the last year that these firms made oodles of money with investment strategies that turned toxic the next year.
And, yeah, we get it – there is a theoretic connection between compensation and performance. But we also know that there’s a difference between theory and practice. Too many of the same employees who either perpetrated the events leading to the meltdown or stood idly by while it happened are still in place.
When AIG finally revealed what they did with the bailout money, we found out that a big chunk of it went overseas. Now, New York Post reporter John Aidan Byrne tells us that the bailout recipients are bailing out – on U.S. workers! Story found that Bank of New York Mellon, Bank of America and Citigroup, all recipients of billions of bailout dollars, are shifting more jobs overseas. The explanation, that nothing in TARP prohibits them from moving jobs out of the US, is so lame I’m surprised Story even bothered to mention it.
The initial indicators of the current financial meltdown were visible in mid-2007. The deeper, underlying causes were recognized, talked about in Washington and then ignored as far back as 2004. The collective memory is short. Nobody wants to hear the bad news, especially when it’s this bad and it goes on for this long. The morning you wake up and wish the financial meltdown would just go away is your most dangerous moment – wishing won’t make it so.
Of the three monitors established by the legislation that created the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP), only one has the authority to prosecute criminals. That is the Office of the Special Inspector General (SIGTARP) whose motto is “Advancing Economic Stability through Transparency, Coordinated Oversight and Robust Enforcement.” The Special Inspector General in charge, Neil Barofsky, told Congress before the recess that he was by-passing the Rogue Treasury to get answers directly from TARP recipients about what they are doing with the bailout money. Now, SIGTARP has set up a hotline (877-SIG2009) for citizens to report fraud or “evidence of violations of criminal and civil laws in connection with TARP.” To date, they have received 200 tips and launched 20 criminal investigations.
What started out as a bailout costing $750 billion quickly turned into $3 trillion – an amount about equal to the U.S. government’s 2008 budget. This week, SIGTARP released a 250-page report in an attempt to place “the scope and scale [of TARP] into proper context” and to make the program understandable to “the American people.” I can’t recommend that you read a report of that length, or even that you download it (more than 10 megabytes) unless you have broadband internet access. (In fact, I don’t understand what makes them think that the American people are going to understand anything that takes 250 pages to explain… Isn’t over-complicating one of the problems they want to solve?) You can get all the high points in Barofsky’s statement to the Joint Economic Committee, which is only 7 pages and a few hundred kilobytes. If you have more time than patience, you can watch the testimony on C-SPAN.
I applaud the hard work of the SIGTARP to provide oversight to Treasury even though they are “currently working out of the main Treasury compound.” Let’s hope they can break free of the hazards associated with the self-regulation that got us into this financial mess in the first place.
Kudos to the Daily Beast for doing its homework and exposing the blatant hypocrisy behind green-tinged celebrity. People like Gore, Streisand, and Madonna have been filling airwaves with exhortations to pitch in and save the planet while living the good life that is supposedly destroying it. Gore himself has put forth a proposal that Professor William Nordhaus has said would ruin the economy. One way for these Green celebs to reduce their carbon dioxide emissions would be to have them stop blowing so much hot air on the topic. There is also the option of listening to the words of Freeman Dyson and stop viewing this thing as a matter of faith. These people should really look more closely at their own lifestyles before telling us how to live. It would be nice if a little of the vitriol could be removed from the debate and we could have a reasonable look at the possible options. Our world and economy are too important. has said would ruin the economy. One way for these Green celebs to reduce their carbon dioxide emissions would be to have them stop blowing so much hot air on the topic. There is also the option of listening to the words of Freeman Dyson and stop viewing this thing as a matter of faith. These people should really look more closely at their own lifestyles before telling us how to live. It would be nice if a little of the vitriol could be removed from the debate and we could have a reasonable look at the possible options. Our world and economy are too important.
The Housing & Economic Recovery Act of 2008 was passed last August. It created the HOPE for Homeowners Program, which the Congressional Budget Office estimated would help 400,000 homeowners to refinance their loans and stay in their homes. Here's a stunning revelation: According to the Federal Housing Authority (FHA), in the first six months since the law was passed, exactly one (1) homeowner refinanced under the program!
You can listen to the story on NPR, "Investors Support Overhauling Homeowner Program". One such investor, PIMCO, supports programs that would reduce the principal balance on mortgages by a small amount in order to keep the cash flow coming from mortgage payments. Given what we know about investment strategies to push companies into bankruptcy in order to benefit from credit default swap payouts, I was initially leery of such statements coming from bond investors. Then I remembered the problem with the paperwork on the mortgages – if bondholders can't prove ownership of the lien the homeowner keeps the house with no further payments. That's when it started to make sense.
Of course, if they can get the homeowners to come in for a re-fi they can correct the paperwork mistakes. It could be worth it to investors without default protection to accept principal reductions – if the homeowner goes into bankruptcy they may not be able to prove they own the mortgage without the new paperwork. With the re-fi, they get all new documentation.
These programs were designed for homeowners who are current on their mortgage payments but whose homes are "underwater", that is, the principal balance on the mortgage is more than the market value of the house. Some can keep up their payments with the hope that the market price of the home adjusts in the distant future; others might benefit by the modest reductions in principal favored by some bond investors. But in a situation described by a Stockton (CA) homeowner the principal reduction is unlikely to be enough – the home is worth $220,000 and the mortgage balance is $420,000. These homeowners' best financial strategy is to take the hit to their credit report and default on the mortgage. Investors like PIMCO might, if their paperwork is good, get half their investment back by taking possession of the property; they'll get it all back if they bought the credit default swap; and they get nothing if the paperwork is screwed up.
How many mortgages are underwater? Bank of America’s annual report says that 23 percent of their residential mortgage portfolio has current loan-to-market value ratios greater than 90 percent. When they include home equity loans in the calculation, totaling lending on a residential property, the share with less than 10 percent equity rises to 37 percent. At the end of 2008, Bank of America held $248 billion in residential mortgages and $152 billion in home equity loans, after taking write-offs of about $4.4 billion last year. On the other hand, Wells Fargo did not specifically report the share of their portfolio with loan-to-market value ratios greater than 90 percent. It’s hard to tell just how many mortgages are how far underwater at an aggregate level. I would imagine that these numbers are being checked in the Treasury’s stress testing of individual banks.
In any event, Congress is not giving up (although we almost wish they would before this gets any worse). The House Committee on Financial Services combined with the House Judiciary Committee has introduced a new bill to improve the old bill's version of Hope for Homeowners. Trying to take it a step further, the House Financial Services Committee is holding hearings on a Mortgage Reform Bill next week. The plan is to set lending standards for all mortgage originators. Chairman Barney Frank (D-MA) is of the view that the "great economic hole" we are in was started by“ policymakers’ distrust of regulation in general, their enduring belief that markets and financial institutions could effectively police themselves."
With this we do agree: self-regulation in financial services is a root cause of our current economic disaster. Until it is completely removed – not just from mortgage lending but from all financial products and services – nothing Congress does will prevent another crisis.
The Tax Foundation calculates the taxes paid per capita, including what is spent by people on average in neighboring states, including state and local fees. The two maps show, first, the tax burden, taxes paid as a percent of income, the second, the difference in the ranks of states in tax burden and in income.
The map for tax burden is colorful, so one might suppose there is a big difference in the local and state burden. There is variation, but the amazing story is how small the differences really are. The variation is from a maximum of 11.8 percent in New Jersey (note that Taxachusetts is in the middle of the pack) to a low of 6.4 percent in Alaska. But most states, 38, are in between 8.6 and 10.2 percent.
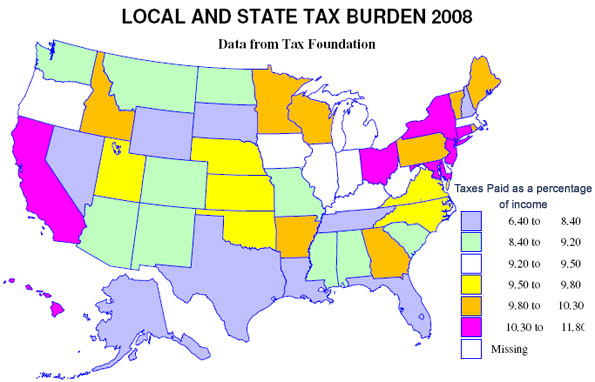
The lowest tax burdens are not surprising – Alaska (6.4) and Nevada (6.6), but the next lowest, Wyoming (7) and Florida (7.4), may be a surprise. The highest tax burdens, as may be expected, are megalapolitan New Jersey, New York (11.7), Connecticut (11.1) and Maryland (10.8), but Hawaii (10.6) in this group may be a surprise. The states in the middle, besides Massachusetts, include a contiguous set centered in Chicago – Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, Kentucky and West Virginia (all 9.3 to 9.5).
The modest range of burdens implies that generally richer states have higher tax burdens and poorer states have lower burdens, but the second map shows that there are many exceptions. Richer states with higher tax burdens include (a small difference in tax and income ranks) District of Columbia, New Jersey, Connecticut, New York and Maryland, and poorer states with a moderately low tax burden are few – Alabama, New Mexico and Montana. Poorer states but with a high tax burden are Arkansas, Kentucky, Utah and Idaho, but this finding perhaps tells us the statistical problem or risk in using per capita rather than per household measures. Strongly Mormon Utah and Idaho, indeed all four states have high average household size, so are not as disadvantaged as the data suggest. For a similar reason, Florida may not be as good as it looks, since it has a quite low average household size.
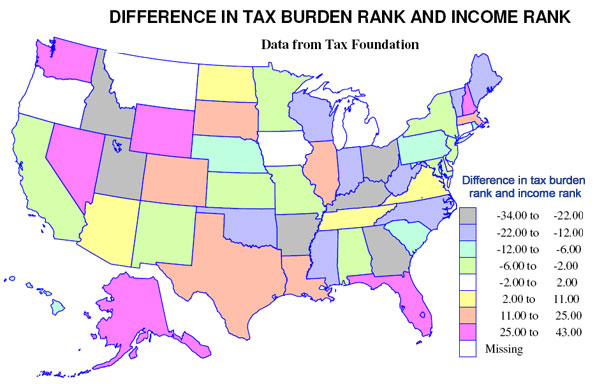
Most interesting may be the richer states with lower ranking tax burdens, notably Wyoming, New Hampshire, Washington and Nevada. Other states with a relatively low burden (lower tax rank than income rank) include Alaska, Colorado, Florida, Massachusetts, and Texas and other states with a relatively high burden (much higher tax rank than income rank) include Georgia, Kentucky, Ohio and West Virginia.
Finally states with close to the same rank in income and tax burden include a set of contiguous Midwestern states, Iowa, Minnesota, Missouri, and Kansas, then Michigan, Oregon and California.
But in sum, choosing a state based on its local and state tax burden could be worth the effort, but the effects by themselves could be more limited than commonly supposed.
Only a few months ago, I admonished Michigan for its hysteria about brain drain. Given the recent news coverage concerning the exodus from the recession-plagued state, you might expect I’m ready to eat some crow. On the contrary, I’m here to report that Michigan has learned nothing from its past mistakes.
Richard Herman, an advocate for increasing rates of immigration to the Rust Belt, posts on his blog the same critique I have aired about how Michigan addresses its talent crisis:
However, the current focus on "brain drain" as the source of the problem misses the real issue.
While no doubt the Midwest economy is causing college grads who might otherwise want to stay home to leave, in an ever more mobile society, moving out is a natural part of people's lives. Indeed, if you read the typical account of how the elite global knowledge worker lives, you often hear about people flitting from place to place to place chasing opportunity.
The real problem is not that too many people are leaving, but rather that too few are coming. It isn't an outflow problem, it's an inflow problem.
The former urban industrial powerhouses of the United States all suffer from the same malaise. Every city is fixated on its local labor pool, asking institutions of education to staff the “factory.” The great irony is that economic growth doesn’t happen without immigration or domestic in-migration. There is no story of a great metropolis that successfully barred its people from leaving.
The tortured metaphor for brain drain stems from private enterprise. But even in the arena of human resources, the concept of churn isn’t an anathema:
The purpose of this article is to open your mind about the silliness of measuring only aggregate turnover. I can think of no better indication of a so-called expert’s lack of true understanding of employee turnover than when I read an article or a book on retention and the author invariably expounds on the need to keep everyone.
The burgeoning narrative is that churn benefits both employee and employer. The same is true for resident and state. Fear of the outsider prevents all parties from making a rational choice and improving human welfare.
Michigan should embrace its out-migration and aggressively seek new residents. I further recommend any reference to “retention” be abolished from official policy. Where, and how many, graduates go is largely immaterial. Instead of Cool Cities to keep Michigan talent instate; what would it take to get the next generation of engineers from Colorado schools or Asia to move to the Rust Belt?
|