For years, the world's busiest airports in passenger volume have been Atlanta's Hartfield-Jackson International and Chicago's O'Hare. However, there are indications that this long dominance may be about to end. According to Airport Council International data for 2009, Chicago O'Hare had fallen to 4th position, following Atlanta, London-Heathrow and Beijing Capital International Airport.
Beijing's Capital International increased its passenger volume by 17% in 2009, while European and American airports were experiencing slight declines due to the recession. Beijing's increase is more significant, because growth might have been expected to level off after the 2008 Olympics, which were held in Beijing. Between 2008 and 2009, Beijing rose from 8th in the world to 3rd, and from 20th place in 2004, when its volumes were approximately one-half the present level.
Early 2010 data (first quarter) indicates that Beijing Capital International has become the second busiest airport in the world, trailing only Atlanta. Passenger volumes were up 10.5% from a year earlier. If the current rate of growth continues, Beijing should pass Atlanta in two to three years, even if the American economy improves.
London's 130 million annual passenger traffic was the greatest of any metropolitan area in the world in 2009 (distributed among five airports). The new Conservative-Liberal Democrat government seems determined, however, to forfeit this ranking, having banned further London airport expansions to combat what it calls "binge flying."
New York was second with passenger traffic of 105 million at its three major airports, while Tokyo was third at 95 million. "Binge flying" does not seem to be a concern in Japan, where Tokyo's Haneda Airport is adding a fourth runway and will soon serve international flights again, providing competition to more distant Narita. Atlanta's single airport handles an annual passenger volume of 88 million.
Other airports in China are also growing. In the Pearl River Delta (the world's largest "mega-region," an area of adjacent urban areas), the four large airports, Hong Kong, Guangzhou and Shenzhen accommodated passenger traffic of more than 105 million in 2009. Traffic at Shanghai's Pudong and Hongqiao grew 14% and 10% respectively.
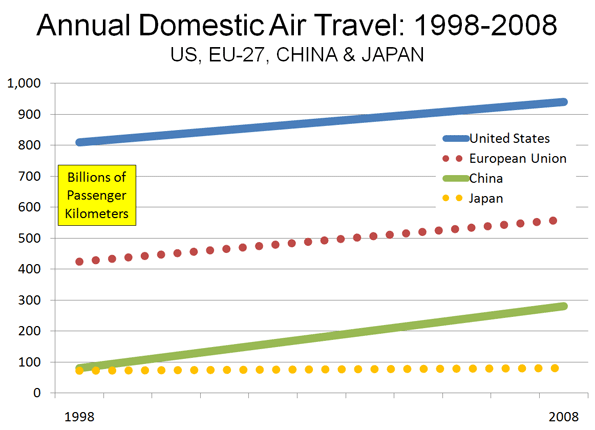
Overall Chinese air traffic is also growing rapidly. Over the past 10 years, annual passenger volumes have risen an average of more than 25%. This compares to an average annual growth rate of 3.2% in the European Union (EU-27), 1.6% in the United States and 1.1% in Japan (Figure). The US continues to be dominant in passenger volumes, at 940 billion annual passenger kilometers, compared to 560 billion in the European Union, 280 billion in China and 80 billion in Japan (data calculated from US, Europe, China and Japan national sources).