
Tokyo-Yokohama continues to be the largest city in the world, with nearly 38 million residents, according to the just released Demographia World Urban Areas (12th Annual Edition). Demographia World Urban Areas (Built-Up Urban Areas or Urban Agglomerations) provides annual estimates of the population, urban land area and urban population density of all identified built-up urban areas in the world. This year's edition includes 1,022 large urban areas (with 500,000 or more residents), with a total population of 2.12 billion, representing 53 percent of the world urban population.
Demographia World Urban Areas uses base population figures, derived from official census and estimates data, to develop basic year population estimates within the confines of built-up urban areas. These figures are then adjusted to account for population change forecasts, principally from the United Nations or national statistics bureaus for a 2016 estimate.
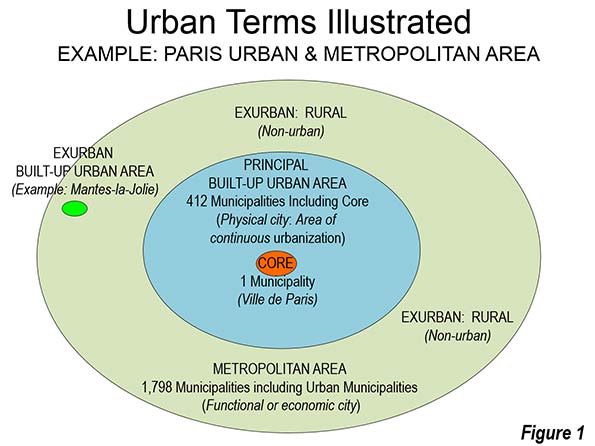
Built-up urban areas are continuously built-up development that excludes rural lands. Built-Up urban areas are the city in its physical form, as opposed to metropolitan areas, which are the city in its economic or functional form. Metropolitan areas include rural areas and secondary built-up urban areas that are outside the primary built-up urban area. These concepts are illustrated in Figure 1, which uses the Paris built-up urban area (unité urbaine) and metropolitan area ("aire urbaine") as an example.
The Largest Cities
The world’s eight largest cities are located in Asia. Tokyo-Yokohama became the largest urban area, according to the United Nations, in 1955, more than 60 years ago. However, Japan’s capital may not old onto the top position for long. With Japan now losing population, it seems likely that Tokyo-Yokohama --- which has been about the only place in Japan gaining population --- will begin shrinking in the next decade, while facing a strong challenge from Jakarta.
Jakarta has closed the gap to about 6.4 million. This may seem like a lot, but this is the closest a number two urban area has been since 1965, when New York trailed Tokyo-Yokohama by 5.1 million. The gap between number one and number two New York amounted to 16.5 million in 1995.
Jakarta has grown very quickly, and now stands at a population of 31.3 million. Between 2000 and 2010, Jakarta added more than 7,000,000 residents, one of the largest population gains of any city in history. Should this growth continue, and the population of Tokyo-Yokohama begin to decline, the largest city in the world could be Jakarta by 2030. Jakarta is also the largest city in size in the southern hemisphere, stretching beyond its city limits, into the regencies of Tangerang, Bogor, Bekasi and Karawang to the large independent cities of Tangerang, South Tangerang, Depok, Bekasi and Bogor.
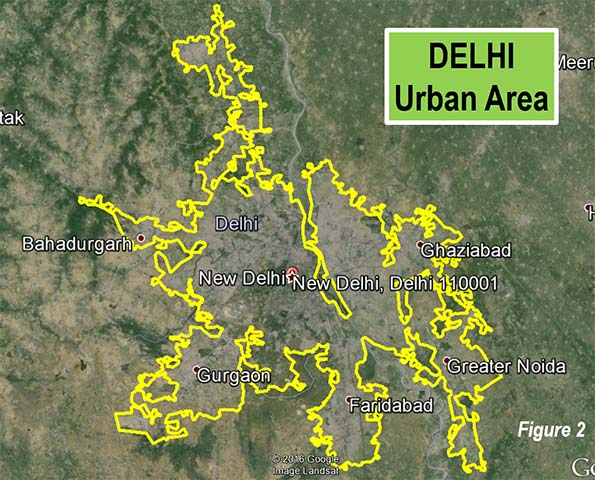
Delhi, India’s capital, is not only the third largest city in the world, but is also the largest in India (25.7 million). That may be surprising, since Mumbai (Bombay) was the largest in India for decades and had been widely touted to become the world’s largest city. Delhi spreads from the National Capital Territory of Delhi into the states of Haryana and Uttar Pradesh. These areas include the modern edge city technology hubs of Gargaon and Noida (Figure 2).
Seoul-Incheon is the fourth largest city in the world, with 23.6 million residents, Seoul-Incheon spreads from the core municipality of Seoul into suburban Gyeonggi and the independent municipality of Incheon. The core city of Seoul has stopped growing, and approximately 60 percent of the population is in the suburbs.
Manila is the fifth largest city, with 22.9 million residents. Manila slipped from the fourth position according to recently obtained Philippine national statistics authority population projections. However, Manila continues to be one of the world's fastest growing megacities and can be expected to pass Seoul-Incheon in the next few years. Manila spreads from the National Capital Territory into the adjoining provinces of Cavite, Laguna, Rizal and Bulacan.
Sixth ranked Mumbai is a new entry to the top 10, with 22.9 million residents. The Mumbai urban area has been redefined to incorporate adjacent urban areas, which explains its larger population relative to last year. Mumbai extends from the municipality of Mumbai into the districts of Thane and Raighar.
The sixth largest city is Karachi in Pakistan's with 22.8 million residents. This population estimate is the least reliable among the largest cities. Pakistan's last population census was nearly 20 years ago, and had been scheduled for March 2016. As of publication, the census has been postponed and no new date set.
Shanghai dropped to the number eight position from sixth place last year. Shanghai's population is estimated at 22.7 million residents. Like many cities across China, population growth has dropped substantially during this decade. Recently, the Shanghai city government announced that the population had fallen slightly over the last year, ending three decades of dramatic population growth in the last three decades. The Shanghai urban area is almost completely confined to the municipality of Shanghai, but has minor extensions into the provinces of Jiangsu and Zhenjiang.
New York is the ninth largest city, with a population of 20.7 million. New York is the largest built-up urban area outside Asia and covers the largest land area of any urban area. New York extends into Long Island and the Hudson Valley in the state of New York, Connecticut and New Jersey. New York had been the world's largest city before Tokyo, a distinction that it had held since 1925, when it surpassed London (now 33rd largest).
The 10th largest city of Sao Paulo, with a population of 20.6 million. Sao Paulo is a new addition to the top 10, Latin America's largest city and the core municipality. Sao Paulo stretches from its large core city in all directions, with approximately half of the population in the suburbs.
Two cities fell out of the top 10, Beijing and Guangzhou-Foshan. Like Shanghai and some other cities of China, newer population estimates indicated a substantial decline in growth rates. Beijing is now the 11th largest city in the world, while Guangzhou-Foshan is 13th largest.
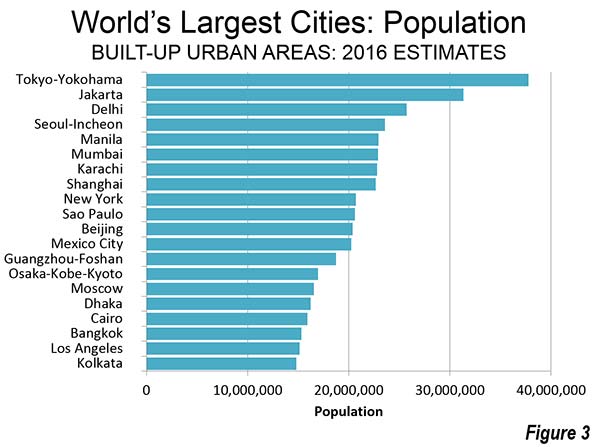
Mexico City is ranked 12th largest in the world. Mexico's capital has experienced a roller coaster ride in urban area rankings since the middle of the last century. In 1950, Mexico City ranked 17th in the world, according to United Nations estimates. By 2000, Mexico City was second in the world to only Tokyo Yokohama. During the period of its greatest growth, in the late 20th century, it was common to hear that Mexico City would eventually be the largest in the world (as was the case with Mumbai, above) but its once frenetic growth has cooled considerably.
Los Angeles has also had its ups and downs. It is substantial growth in the first half of the 20th century brought Los Angeles from virtually nowhere to 12th largest in the world by 1950. As in Mumbai and Mexico City, there were those who expected Los Angeles to become the largest city in the world. By 1965, Los Angeles was the sixth largest city, trailing only Tokyo Yokohama, New York, Paris, London and Osaka Kobe Kyoto. Now, Los Angeles has fallen to 19th position and not only is unlikely to ever be the largest city in the world or even in the United States.` The 5 million population gap compared to New York in 2016 is little different from 1990.
Distribution of Population
Much has been made of the fact that the world now has more than one half of its population living in urban areas. More than one analyst has misunderstood this as meaning that the norm for world residents looks like Fifth Avenue in New York, central London or Paris or the huge shantytowns of Mumbai or Dhaka. In fact, however, most urban residents live in nothing like such environments (See: What is a Half Urban World?).
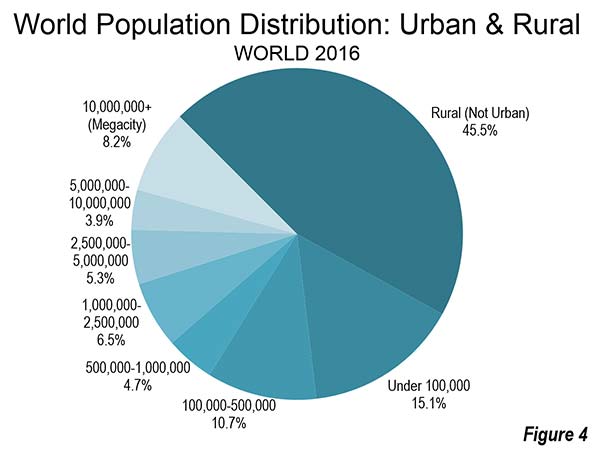
Only 8.2 percent of the world population lives in megacities (built-up urban areas with more than 10 million population. In contrast nearly a quarter lives in cities of more than 1 million population, including the megacities. A larger 30 percent of the world population lives in urban areas under 1 million population, which includes the smallest towns. Rural areas still have nearly 46 percent of the world population (Figure 3).
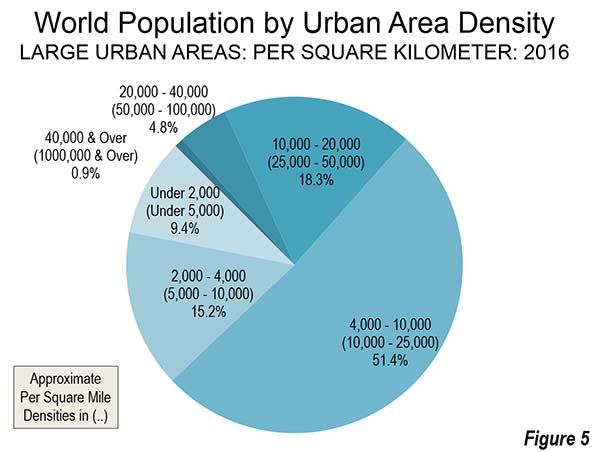
Most of the large built-up urban area population lives at densities between 4,000 and 10,000 per square kilometer, or approximately 10,000 to 25,000 per square mile. These population densities are typical in parts of Asia, Africa and South America. Another one quarter of the population lives at densities of below 4,000 per square kilometer or approximately 10,000 per square mile. These densities are principally found in Europe, North America and Oceania (principally Australia and New Zealand). Slightly less than one quarter of the population lives at higher densities, above 10,000 per square kilometer or 25,000 per square mile. These densities are largely limited to certain Asian and African nations, such as Bangladesh, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Pakistan (Figure 4).
The Future
As has been noted before, much of the population growth in the world will be in Africa over the next century. However, in the next few decades the greatest urban population growth seems likely to be in Asia, where 57 percent of the large urban area population lives. Even with declining growth rates, such as in China, many millions more rural residents are expected to continue moving into China’s cities .
Note on Availability
The full Demographia World Urban Areas and its components can be downloaded as follows:
Full Report:
By Component:
Demographia World Urban Areas- Index
Photograph: Cover of Demographia World Urban Areas: 12th Annual Edition
Wendell Cox is principal of Demographia, an international pubilc policy and demographics firm. He is a Senior Fellow of the Center for Opportunity Urbanism (US), Senior Fellow for Housing Affordability and Municipal Policy for the Frontier Centre for Public Policy (Canada), and a member of the Board of Advisors of the Center for Demographics and Policy at Chapman University (California). He is co-author of the "Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey" and author of "Demographia World Urban Areas" and "War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life." He was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission, where he served with the leading city and county leadership as the only non-elected member. He served as a visiting professor at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, a national university in Paris.












