
Estonians and Latvians are the only independent nations in Europe with fewer people now than at the beginning of the 20th century. It is written in The White Book, 2004, about losses inflicted on the Estonian nation by occupation regimes. During the whole period (1940-1991) nearly 90,000 citizens of the Republic of Estonia perished, and about the same number of people left their homeland forever. It happened in a nation with a population number of about one million. Another nation, through centuries, gradually perished and disappeared from this territory: the Livonians. Their leader, Caupo, in 1203 was received with honor by Roman Pope Innocent III. Interestingly, at least three regions in America are named after Livonians. They are Livonia in New York State, Livonia in Pennsylvania, and Livonia in the Michigan. Do the inhabitants of these Livonias have any connection to the Livonians at the Baltic Sea?!
The growth of the number of Estonians in 45 postwar years till 1990 was about 100 thousand. This was caused by natural increase, decrease of mortality, return of ethnic Estonians from Russia. The fertility rate of Estonians was below the replacement level for 40 years, but from 1970 to 1990 was at or above the replacement level. At the same time, the foreign-born population experienced a rate of fertility beneath the replacement level: 1.64 - 1.72.
The time between 1983 and 1988 was a positive period, with a crude birth rate (the number of births per 1000 people per year) of about 16.0. It is interesting that this situation arose during the so-called “stagnation era”. The stagnation period – life without radical changes – was probably fruitful for fertility growth. The same trend was noted for Russia. Perhaps this increase was caused by the decision of the Soviet government in 1981 to increase the birth rate “About Measures of Public Support to Families Having Children”. In 1989, the peak of fertility was over.
The French demographer Adolphe Landry (1874-1956) defined genuine demographic revolution as the situation in which use of contraceptives and abortions by women becomes universal. This revolution detaches fertility from social control and transfers it to the interests of individuals. For Estonia, this period arrived at the beginning of nineties, when plenty of contraceptives became available, in addition to abortions continuing to be permitted.
In 1991, the crude birth rate fell to 12.4, and the total fertility rate (number of children per woman during her lifetime, which characterize the necessary replacement level of 2.1) to 1.80. The year of 1991 was the first year of two decades of continuing decrease. Remarkably, fall of the birth rate at the beginning of nineties was much worse than it was during WW II. The population of about one million had 19.5 and 19.2 thousand births respectively in 1941 and 1942 during the war, but in 1993, when conditions were clearly better, only 15.3 thousand children were born to a population of one and a half million. The genuine demographic revolution had truly arrived!
The reasons, in addition to the availability of contraceptives and abortions, were the decline of religion, economic uncertainty regarding the future, the opening of the world with a variety of lifestyle choices and career paths. Almost thirty decrees regarding the family benefits of the Soviet period that had been made by that government were cancelled in 1992. In the liberal market economy of the nineties, population policy was left largely to chance. Public attention to the issue was narrowly limited to family benefits and integration programs.
The Parental Benefit Act passed in 2003 tried to attain the birth rate. According to the Act, persons have the right to receive parental benefits for 435 days from the day following the final day of maternity leave. The amount of the parental benefit received is calculated on the basis of the Social Tax paid during the previous year. If the parent didn’t work, the parental benefit is paid at the designated benefit base rate, which is 290 euros in 2013. The upper limit of the amount of the parental benefit is three times the average salary earned during the year before last, which – in 2013 – is 2,234 euros.
If we take the birth rate of the years 2002 and 2003 – 13,000 births – as the plateau (base rate) and eliminate all other factors pertaining to reproductive behavior, then natality during the 2004-2012 period resulted in about 18 thousand additional births. This speaks to the effectiveness of the parental benefit. However, even this was insufficient for attaining positive natural increase. The total maximum fertility rate obtained was 1.65, but later, in 2011, it decreased to 1.52. In 28 countries of European Union the mean value of the total fertility rate was 1.58 in 2012, for euro area it was 1.56. However in France, which has perhaps the oldest experience in field of demography and demographic research, this indicator was 2.01. In contrast, Singapore's total fertility rate steadily dropped from 1.6 in 2000 to a record low of 1.16 in 2010. It bounced back to 1.2 in 2011, and further to 1.29 in 2012, but last year slipped again to 1.19.
The government aims, by 2015, to achieve a birth rate that is higher than the death rate, meaning an increase of the total birth rate to 1.70. (Action Program of the Government of the Republic 2011-2015). This seems unattainable. Poverty and migration worsen the situation. The at-risk-of-poverty rate in Estonia in 2011 was 17.6% on the average. The parent benefit and family benefits together constituted 1,7% of GDP in 2011 ( the same figure in Sweden and Finland was 3%).
One key cause, ironically, is freedom to move that came with the fall of the Soviet Union. Handling the population decrease we described first of all the birth rate, but last years has been intensified external migration. Migration that took place in 2011 decreased the population of Estonia in 2012 by 6,600 inhabitants. The trend continued. In external migration, there was an increase in both immigration and emigration in 2012. Over 4,000 persons immigrated to and almost 11,000 persons emigrated from Estonia. The main destination countries for emigrants are Finland and the United Kingdom. Most of the immigrants are in fact returnees, mostly from Finland. The second place is held by Russia, but the immigrants from Russia are mainly new immigrants.
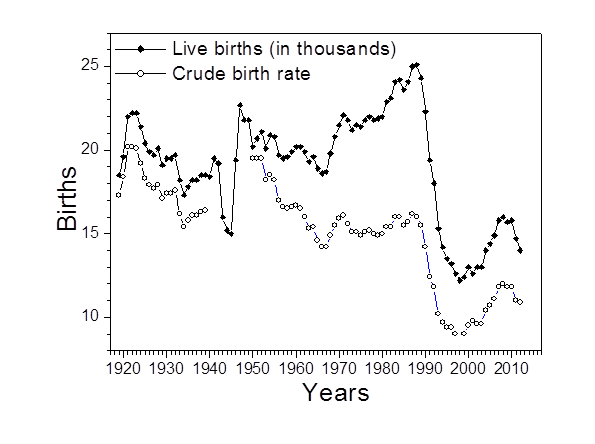
Despite numerous attempts to boost birth rate, the years from 1991 to 2013 are characterized by a birth rate under the replacement level. The lowest point arrived in 1998, with a total fertility rate of 1.28. After that it began to rise, reaching 1.65 in the year of 2008, only to decrease again later. At the same time, the population figure decreased by 14%. Problems caused by decreasing population entail a threat to the survival of the Estonian national culture, issues with sustainable economic development and difficulties with the sustainability of the social infrastructure.
How to avoid the fate of Livonians? Is there a force majeure against the small nation? Or it is a problem of insufficient national steering without any specialized institution responsible on population?
Jaak Uibu, a Phd. in human micro ecology, was former Deputy Minister of Health of Estonia and advisor to Minister of Population.
Oleviste photo by E. Kanash.













Immigrants
Estonia needs to encourage immigration.
From India, Africa and wherever else people want to come from.
I read this blog from Estonia http://shaan.typepad.com/ and have not seen many encouraging signs.
Dave Barnes
+1.303.744.9024