Senior citizens (age 65 and over) are dispersing throughout major metropolitan areas, and specifically away from the urban cores. This is the opposite of the trend suggested by some planners and media sources who claim than seniors are moving to the urban cores. For example, one headline, "Millions of Seniors Moving Back to Big Cities" is at the top of a story with no data and anecdotes ranging that are at least as much suburban (Auburn Hills, in the Detroit area) and college towns (Oxford, Mississippi and Lawrence, Kansas), as they are big city. Another article, "Why Seniors are Moving to the Urban Core and Why It's Good for Everyone," is also anecdote based, and gave prominence to a solitary housing development in downtown Phoenix (more about Phoenix below).
Senior Metropolitan Growth Trails National
Between 2000 and 2010, the nation's senior population increased approximately 5.4 million, an increase of 15 percent. Major metropolitan areas accounted for approximately 50 percent of the increase (2.7 million) and also saw their senior population increase 15 percent. By contrast, these same metropolitan areas accounted for 60 percent of overall growth between 2000 and 2010, indicating that most senior growth is in smaller metropolitan areas and rural areas.
Senior Metropolitan Population Dispersing
The number of senior citizens living in suburbs and exurbs of major metropolitan areas (over 1,000,000 population) increased between 2000 and 2010, according to census data. The senior increases were strongly skewed away from the urban cores. Suburbs and exurbs gained 2.82 million senior residents over the period, while functional urban cores lost 112,000. The later suburbs added 1.64 million seniors. The second largest increase was in exurban areas, with a gain of 0.88 million seniors. The earlier suburbs (generally inner suburbs) added just under 300,000 seniors (Figure 1).
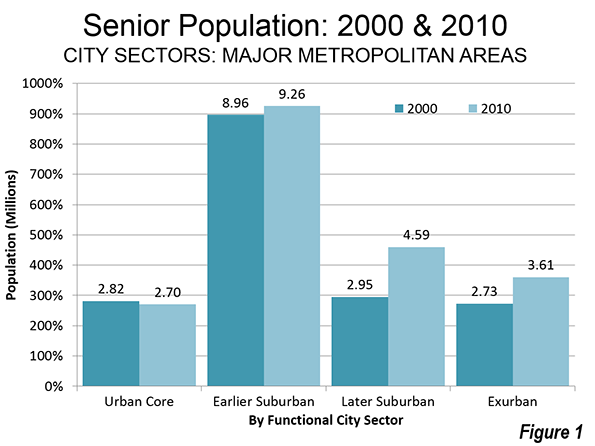
During that period, the share of senior citizens living in the later suburbs increased 35 percent. The senior citizen population share in the exurbs rose nearly 15 percent. By contrast, the share of seniors living in the functional urban cores declined 17 percent. Their share in the earlier suburbs declined 11 percent.
This is based on an analysis of small area data for major metropolitan areas using the City Sector Model.
City Sector Model analysis avoids the exaggeration of urban core data that necessarily occurs from reliance on the municipal boundaries of core cities (which are themselves nearly 60 percent suburban or exurban, ranging from as little as three percent to virtually 100 percent). It also avoids the use of the newer "principal cities" designation of larger employment centers within metropolitan areas, nearly all of which are suburbs, but are inappropriately joined with core municipalities in some analyses. The City Sector Model" small area analysis method is described in greater detail in the Note below.
Pervasive Suburban and Exurban Senior Gains
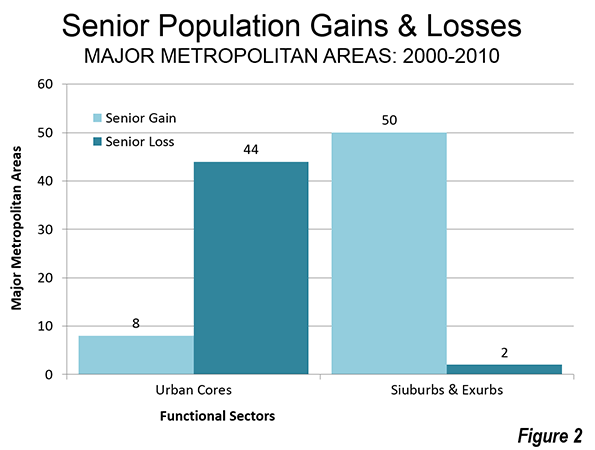
The gains in functional suburban and exurban senior population were pervasive. Among the 52 major metropolitan areas, there were gains in 50. In two areas (New Orleans and Pittsburgh), there were losses. However, in each of these cases there was an even greater senior loss in the functional urban cores. In no case did urban cores gain more or lose fewer seniors than the suburbs and exurbs. Eight of the functional urban cores experienced gains in senior population, while 44 experienced losses (Figure 2)
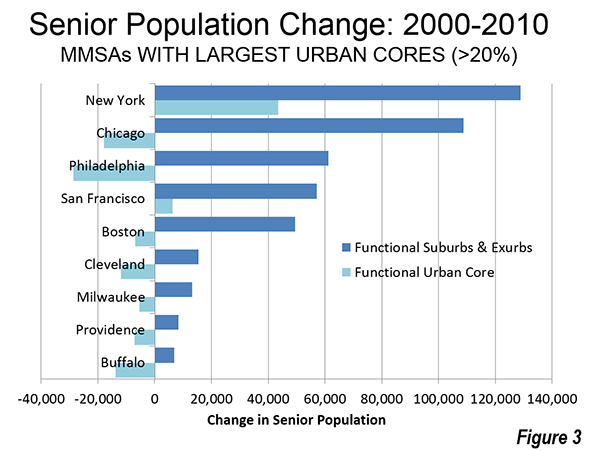
Largest Urban Cores
The major metropolitan areas with the largest urban cores (more than 20 percent of the population in the functional urban cores), would tend to be the most attractive to seniors seeking an urban core lifestyle. But they still saw their seniors heading to the suburbs and exurbs (Figure 3). Senior populations declined in the functional urban cores of all but two of these nine areas, New York and San Francisco. However, in both of these metropolitan areas, the increases in suburban and exurban senior populations overwhelmed the increases in the urban cores. All of these nine major metropolitan areas experienced increases in their suburban and exurban senior populations.
Moreover, the Phoenix anecdote cited above is at odds with the reality that the later suburbs and exurbs gained 165,000 seniors between 2000 and 2010. The earlier suburbs lost 7,000 seniors (No part of Phoenix has sufficient density or transit market share to be classified as functional urban core).
Consistency of Seniors Trend with Other Metropolitan Indicators
As has been indicated in previous articles, there continues to be a trend toward dispersal and decentralization in US major metropolitan areas. There was an overall population dispersion from 1990 to 2000 and 2000 to 2010, which continued trends that have been evident since World War II and even before, as pre-automobile era urban cores have lost their dominance. Jobs continued to follow the suburbanization and exurbanization of the population over the past decade away as cities became less monocentric, less polycentric and more "non-centric." As a result, work trip travel times are generally shorter for residents where population densities are lower. Baby boomers and Millennials have been shown to be dispersing as well, despite anecdotes to the contrary (Figure 4). The same applies to seniors.
Note: The City Sector Model allows a more representative functional analysis of urban core, suburban and exurban areas, by the use of smaller areas, rather than municipal boundaries. The more than 30,000 zip code tabulation areas (ZCTA) of major metropolitan areas and the rest of the nation are categorized by functional characteristics, including urban form, density and travel behavior. There are four functional classifications, the urban core, earlier suburban areas, later suburban areas and exurban areas. The urban cores have higher densities, older housing and substantially greater reliance on transit, similar to the urban cores that preceded the great automobile oriented suburbanization that followed World War II. Exurban areas are beyond the built up urban areas. The suburban areas constitute the balance of the major metropolitan areas. Earlier suburbs include areas with a median house construction date before 1980. Later suburban areas have later median house construction dates.
Urban cores are defined as areas (ZCTAs) that have high population densities (7,500 or more per square mile or 2,900 per square kilometer or more) and high transit, walking and cycling work trip market shares (20 percent or more). Urban cores also include non-exurban sectors with median house construction dates of 1945 or before. All of these areas are defined at the zip code tabulation area (ZCTA) level.
----
Wendell Cox is principal of Demographia, an international public policy and demographics firm. He is co-author of the "Demographia International Housing Affordability Survey" and author of "Demographia World Urban Areas" and "War on the Dream: How Anti-Sprawl Policy Threatens the Quality of Life." He was appointed to three terms on the Los Angeles County Transportation Commission, where he served with the leading city and county leadership as the only non-elected member. He was appointed to the Amtrak Reform Council to fill the unexpired term of Governor Christine Todd Whitman and has served as a visiting professor at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Metiers, a national university in Paris.
Photo: Later Suburbs of Cincinnati (where most senior growth occurred from 2000 to 2010). By Author













As an old fart
I am an old fart and I live (by choice and love it) in the urban core (a 1900 street car suburb).
Easy access to medical (hospitals) care.
Significantly reduced auto usage. Walk 3 blocks to supermarket.
Tons of restaurants. Have walked to 100+.
Lots of exciting young people.
Politically liberal (almost socialist).
Anecdotal, yes.
Dave Barnes
+1.303.744.9024